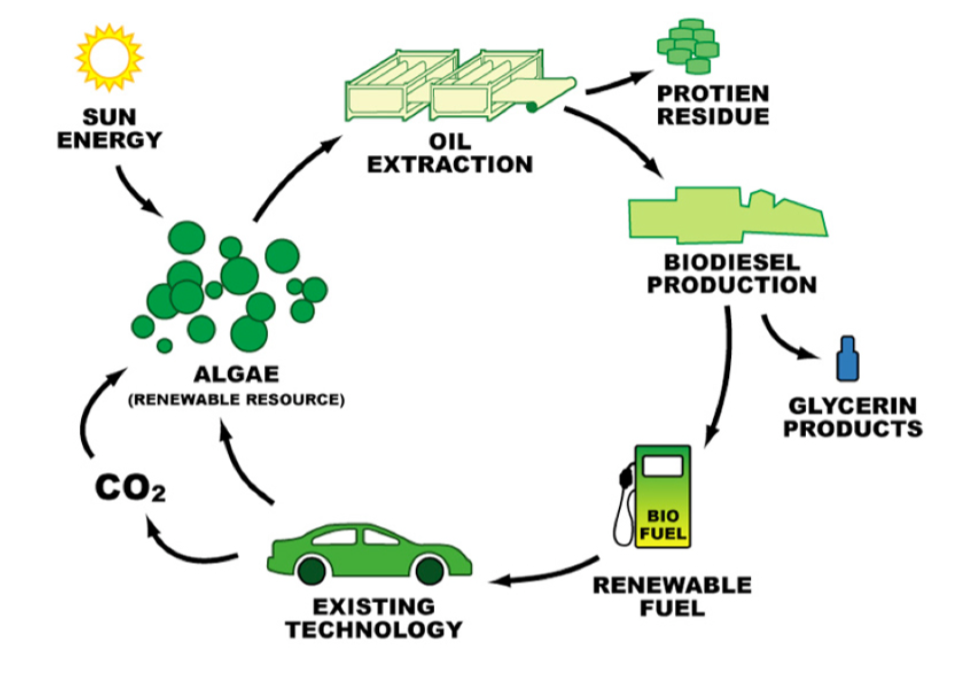
Biofuel is a flammable fuel made from biomass, in simple terms, living plant material. When people say “biofuel,” they usually mean liquid fuels like ethanol and biodiesel, which serve as alternatives to petroleum-based fuels like gasoline, diesel, and jet fuel.
There are two main types of biofuels:
- Ethanol – a form of alcohol, usually made from crops like corn or sugarcane.
- Biodiesel – made by extracting oil from plants and seeds, and then processing it through something called trans-esterification (fancy word, simple concept).
Ethanol can be blended with gasoline, while biodiesel works in a regular diesel engine. Energy-wise, a gallon of biodiesel gives you about 93% of the energy of diesel, and a gallon of ethanol delivers around 73% of what you’d get from gasoline.
Renewable Energy Source
The great thing about biofuels? They grow back.
Unlike fossil fuels, which take millions of years to form under extreme pressure and heat, biofuels are made from stuff we already grow, toss away, or harvest regularly. We’re talking crops, agricultural waste, algae, and even household scraps.
Most bioethanol comes from corn or sugarcane, which can be replanted and regrown in a single season. Compare that to crude oil, which took the dinosaurs and half a planet’s worth of pressure to make, and you’ll see why biofuels are gaining ground.
Fossil fuels are disappearing fast, and once they’re gone, they’re gone. Biofuels? We can grow more next season. It’s not magic, it’s just smart farming with a cleaner outcome.
Reducing Greenhouse Gas Emissions
Call it climate change or global warming, whatever name you give it, we all know it’s a growing problem.
Now, burning fuel from fossil sources pours carbon dioxide and other nasty gases into the air. But biofuels burn cleaner. According to the U.S. Department of Energy, bioethanol can cut greenhouse gas emissions by 40–50% compared to gasoline. Biodiesel can reduce emissions by up to 80% compared to standard diesel.
That’s a huge leap. And since plants absorb carbon dioxide while growing, they’re sort of canceling out part of what’s released when the fuel is burned. It’s not a perfect system, but it’s a lot better than drilling and spilling our way through crude oil.
Economic Benefit
Here’s the kicker: biofuel often costs about the same as gasoline at the pump. But the hidden savings? They stack up.
Because biofuels burn cleaner, there’s less pollution, which means less damage to engines, fewer health issues caused by emissions, and a lighter load on environmental cleanup costs.
And for countries that don’t have massive oil fields under their soil, biofuels offer a homegrown energy option. No more betting your economy on foreign oil prices. Instead, you invest in local farmers and industries, boosting the economy from the ground up literally.
Future Outlook
Let’s be real, fossil fuels won’t last forever. One day, the oil wells will run dry, and gas prices will shoot up faster than a rocket with caffeine.
That’s where biofuels shine. We already have the tools, the land, and the know-how to make them. Why wait for a fuel crisis when we can plant our way out of it?
Imagine fields of sunflowers, soybeans, or algae powering the trucks, planes, and cars of tomorrow. The possibilities aren’t just promising, they’re planting themselves right in front of us.
Best part? Biofuels don’t come in one flavor. We can make them from different crops, waste, and even some creative blends we haven’t dreamed up yet. Compared to fossil fuels, biofuels offer way more flexibility and fewer long-term regrets.