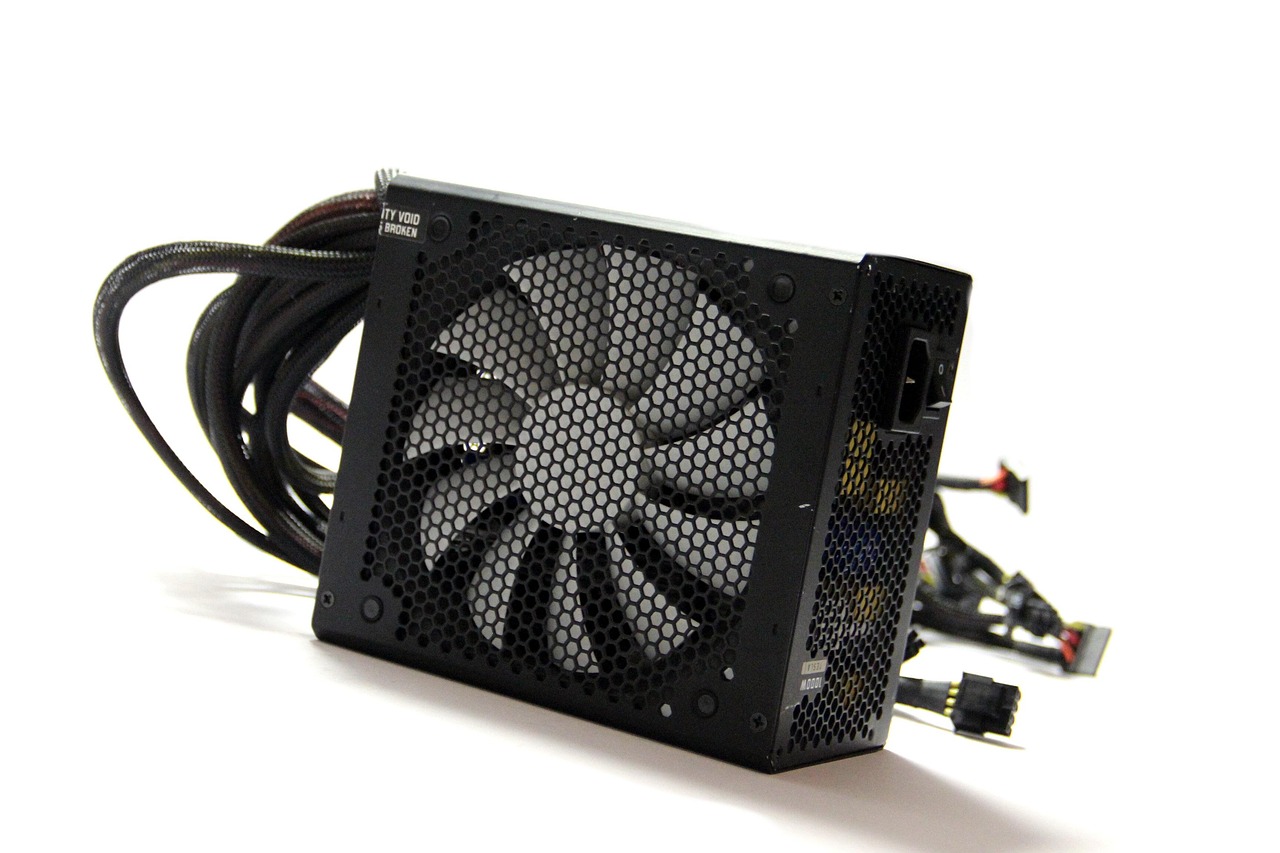
Ever wondered how your PC, smart TV, or gaming rig gets just the right amount of power? The secret sauce is often the SMPS, short for Switched Mode Power Supply. It might sound like something out of a science textbook, but it’s one of the most important—and underrated—components in any modern electronic device.
What Is an SMPS and How Does It Work
Let’s break it down.
An SMPS is an electronic device that efficiently converts electrical power from one voltage level to another. Whether you’re dealing with 110V in the U.S. or 220V in Europe, an SMPS steps it down (or up) to exactly what your device needs, without wasting much energy.
In short:
- It takes in AC or DC power,
- Processes it at high frequencies through a series of switches and transformers,
- And spits out a clean, stable DC voltage for your electronics.
This high-speed switching is what gives SMPS its name and its efficiency edge.
Why Would You Use an SMPS?
The real question is—why wouldn’t you?
From home gadgets like smart speakers and LED TVs to industrial machines and servers, SMPS is the go-to solution when you need:
- Compact size
- High efficiency
- Minimal heat output
And let’s face it, in the age of compact devices and tight spaces, you don’t want a power supply the size of a car battery.
SMPS vs Linear Power Supply: What’s the Difference?
Here’s where it gets interesting. You might have heard of linear power supplies, those older, bulkier units that hum like your grandmother’s fridge. How do they compare to SMPS?
🔌 SMPS (Switched Mode Power Supply):
- High-frequency operation (40kHz+)
- Smaller, lighter transformers (usually ferrite core)
- Much higher efficiency (typically 70–95%)
- Less heat and better voltage regulation
- Ideal for modern electronics
🧱 Linear Power Supply:
- Operates at low frequency (50–60Hz)
- Requires larger, heavier transformers (iron core)
- More heat, less efficiency
- Still good for audio gear (some audiophiles swear by them)
- Old school but reliable
In tech terms, it’s like comparing a Tesla to a diesel truck; both get the job done, but one’s built for the times.
Advantages and Disadvantages of SMPS
Let’s weigh the pros and cons like a responsible buyer (or builder):
✅ Advantages:
- Compact and lightweight — fits almost anywhere
- High efficiency — converts more energy, wastes less.
- Supports a wide range of voltages — very flexible
- Lower heat output — fewer fans, quieter operation
⚠️ Disadvantages:
- More complex circuitry — tougher to repair
- Can introduce noise or glitches if not well-designed
- Harmonic distortion might affect sensitive equipment.t
- Control isn’t as straightforward as in linear suppli.es
That said, modern SMPS designs are solid enough that these drawbacks rarely cause real problems unless you cheap out on a no-name brand from a sketchy online store.
Inside the Circuit: How an SMPS Works
An SMPS doesn’t just throw power around. It uses a clever setup of electronic components, including:
- Rectifiers to convert AC to DC
- High-frequency switches (MOSFETs or IGBTs)
- Transformers to adjust voltage levels
- Filters to clean the output signal
This smart combo delivers a steady DC voltage while being more efficient than your average coffee machine. It’s basically power conversion, leveled up.
The History of SMPS: Where Did It Come From?
Let’s rewind a bit.
- 1836: Inductive coils were already used in experiments to create high-voltage sparks.
- 1958: IBM played around with a transistor-based SMPS for early computing hardware.
- 1959: At Bell Labs, Mohamed M. Atalla and Dawon Kahng invented the power MOSFET, a huge leap for SMPS tech.
- Around the same time, General Motors got in on the action with SMPS patent filings of their own.
Fast-forward to today, and SMPS is practically everywhere, from your laptop charger to data centers running AI workloads.
Where You’ll Find SMPS in Everyday Life
Here are some common places SMPS shows up, often quietly doing its thing:
- Desktop computers and gaming rigs
- Laptop chargers
- LED lighting systems
- Televisions and smart displays
- Phone chargers and USB power bricks
- Industrial control systems
- Battery chargers and power tools
If it plugs in and doesn’t weigh a ton, it probably uses an SMPS.
Final Thoughts: The Unsung Hero of Modern Power
While most people obsess over CPUs and GPUs, the SMPS sits in the background, quietly delivering just the right amount of juice to keep your devices humming. It’s one of the most efficient, compact, and powerful innovations in modern electronics.
So the next time you boot up your PC or charge your phone, give a little mental nod to the SMP, S it’s doing a lot more than you think.